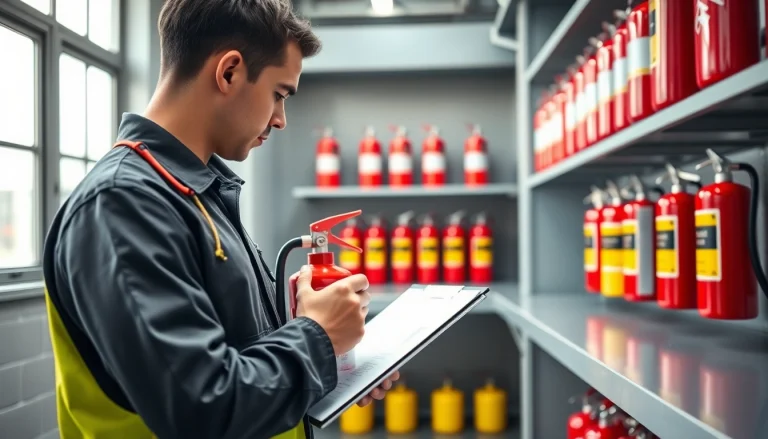
Understanding Fire Extinguisher Servicing
Fire extinguishers are essential safety devices that protect lives and property from the devastating effects of fires. However, these devices require regular maintenance and servicing to ensure they function correctly when needed. Fire extinguisher servicing is more than just a regulatory requirement; it is a critical component of any fire safety strategy. This article delves into the ins and outs of fire extinguisher servicing, covering aspects such as its importance, the types of extinguishers, inspection guidelines, and best practices for maintenance.
1. What Is Fire Extinguisher Servicing?
Fire extinguisher servicing involves a series of tasks designed to maintain the operational readiness of fire extinguishers. This includes regular inspections, testing, and recharging of extinguishers as well as repairs or replacements when necessary. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) recommends specific guidelines and timelines for servicing, which can vary based on the type of extinguisher and its usage. Basic servicing usually entails:
- Routine visual inspections to check for damage and ensure proper placement.
- Annual maintenance checks conducted by certified professionals.
- Hydrostatic testing, required every 5 to 12 years depending on extinguisher type.
- Recharging extinguishers after use or when pressure falls below required levels.
2. Importance of Regular Maintenance
The significance of regular fire extinguisher servicing extends beyond compliance with laws; it is about safeguarding lives. A fully operational fire extinguisher can mean the difference between minimal fire damage and catastrophic loss. Here are the key reasons why regular maintenance is crucial:
- Ensures Reliability: Regular servicing ensures that extinguishers will work when needed, preventing failures during emergencies.
- Compliance: Many jurisdictions require businesses to adhere to fire safety regulations. Failing to comply can result in fines and legal liabilities.
- Cost-Efficiency: Regular maintenance can prevent costly repairs and replacements down the line, as well as potential damage to property.
- Increases Safety Awareness: Regular maintenance encourages businesses to foster a culture of safety among employees, enhancing overall fire safety preparedness.
3. Who Should Perform the Servicing?
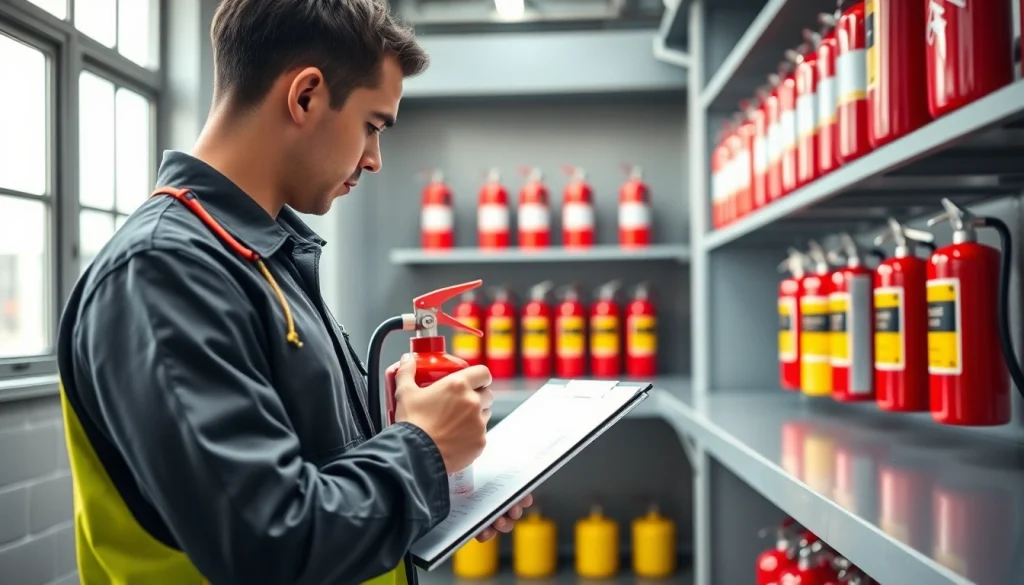
Fire extinguisher servicing should be performed by certified professionals who understand the complexities of different extinguishing agents and mechanisms. While some basic maintenance tasks can be carried out by the staff (such as monthly visual inspections), comprehensive servicing—including pressure testing and refilling—must be completed by licensed technicians. This expertise ensures compliance with local regulations and NFPA standards. Companies like [Cintas](https://www.cintas.com/fire-protection-services/fire-extinguishers/) and [Koorsen Fire & Security](https://blog.koorsen.com/how-is-a-fire-extinguisher-serviced) offer these specialized services, ensuring that your fire extinguishers are properly maintained and functional.
Types of Fire Extinguishers and Their Servicing Needs
Fire extinguishers come in various types, each designed for specific classes of fires. Understanding these types and their servicing needs is essential for proper maintenance.
1. Water, Foam, and Dry Chemical Extinguishers
Water and foam extinguishers are typically used for class A fires involving ordinary combustibles like wood and cloth. Dry chemical extinguishers can combat class A, B (flammable liquids), and C (electrical) fires.
- Servicing Frequency: These extinguishers should undergo annual service by a professional and be recharged after each use.
- Key Checks: Look for damage to the cylinder, gauge readings, and corrosion, and ensure that seals and connections are intact.
2. CO2 and Wet Chemical Extinguishers
Carbon dioxide (CO2) extinguishers are effective for electrical fires and flammable liquids, while wet chemical extinguishers are specially designed for class K fires (common in commercial kitchens).
- Servicing Frequency: Both types require annual inspections, with CO2 extinguishers needing hydrostatic testing every 5 years.
- Key Checks: Inspect the nozzle for blockages, ensure the pressure gauge is within the operational range, and verify that the discharge horn is not damaged.
3. Specialized Recharging Requirements
All fire extinguishers have unique recharging requirements based on their extinguishing agents. Following a discharge or following an inspection:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that your servicing provider follows all regulations regarding recharge procedures.
- Documentation: Keep records of all servicing events and recharges for compliance and safety audits.
Fire Extinguisher Inspection Guidelines
Regular inspections are critical for maintaining fire extinguishers. Establishing a robust inspection process guarantees that all extinguishing devices are functional.
1. Monthly Inspections: Step-by-Step
Monthly inspections can be conducted by any staff member trained in fire safety. A typical inspection process should include:
- Check that the extinguisher is easily accessible and visible.
- Ensure the pressure gauge is within the green zone, indicating proper pressure levels.
- Look for signs of physical damage, corrosion, or leaks.
- Verify that the safety pin and tamper seal are intact.
Record your findings on the inspection tag or logbook to maintain compliance with NFPA regulations.
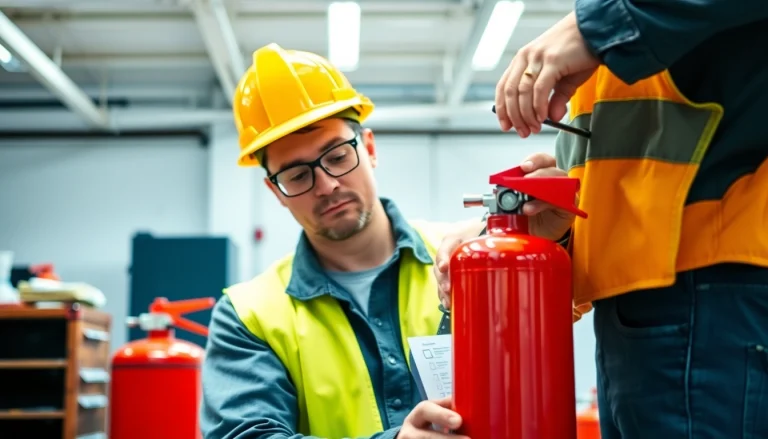
2. Annual Maintenance Checks
Annual maintenance checks should be conducted by certified professionals. This involves a comprehensive examination of the extinguisher and includes the following tasks:
- Pressure testing of the cylinder.
- Replacing any defective parts, such as the nozzle or valves.
- Cleaning the external surface and making any necessary repairs.
- Documenting the service and updating tags or stickers as required.
3. Understanding Inspection Tags and Documentation
Inspection tags and documentation play a crucial role in maintaining fire extinguishers. Ensure that each extinguished device has:
- An inspection tag that is updated following each inspection.
- A maintenance record detailing service dates, findings, and the technician’s signature.
- All records are easily accessible for both internal audits and regulatory inspections.
Common Issues Found During Fire Extinguisher Servicing
During servicing, technicians may encounter various issues that need to be addressed immediately to ensure the functionality of fire extinguishers.
1. Signs of Damage or Expiry
Visible damage or expired extinguishers can severely impact performance. Technicians should look for:
- Visible cracks or dents on the cylinder that can affect pressure retention.
- Corrosion that can weaken the cylinder’s integrity.
- Expired units that need replacement, particularly those exceeding their hydrostatic test interval.
2. Malfunctioning Components
Common malfunctions can impede fire extinguisher operation:
- Blockages in the nozzle that can prevent discharge.
- Faulty pressure gauges that can give false readings.
- Damaged seals that may cause leaks.
3. Understanding Recharge and Replacement Needs
Knowing when to recharge or replace extinguishers is crucial for safety. Here are guidelines to follow:
- Recharge extinguishers after any use, as even a partial discharge can reduce effectiveness.
- Determine replacement needs based on age; the NFPA recommends replacing stored pressure fire extinguishers every 12 years.
- Keep a maintenance record to track when services are needed and to ensure compliance.
Best Practices for Fire Extinguisher Servicing
Following best practices can streamline the fire extinguisher servicing process and enhance overall safety for users.
1. Creating a Servicing Schedule
Establishing a clear servicing schedule is crucial to ensure no extinguisher goes unchecked. Key elements to include are:
- Document scheduling dates for monthly inspections and annual audits.
- Utilize reminders for technicians for hydrostatic tests and recharges.
- Review servicing logs regularly to ensure compliance with local laws.
2. Training Staff on Fire Safety
Staff should be trained in basic fire safety protocols, including the proper use of extinguishers. Components to include in training are:
- Understanding different types of fire extinguishers and their applications.
- Procedures for conducting monthly inspections.
- Emergency protocols and escaping strategies in case of fire.
3. Keeping Records of Maintenance
Maintaining detailed records of servicing activities is essential for compliance and safety audits. This includes:
- Documenting all inspections, maintenance, and repairs.
- Keeping records of technician qualifications and certifications.
- Tracking extinguisher location and service history for each device.
In conclusion, effective fire extinguisher servicing encompasses regular inspections, thorough maintenance checks, and a well-informed staff. As fires can occur unpredictably, ensuring that fire extinguishers are fully operational can significantly minimize risks associated with fire emergencies. By following the outlined guidelines and engaging qualified professionals for servicing, you contribute to a safer environment for everyone.